Art is an attempt to find new solutions to the problems posed by life.
Biography
Francis Bacon was born in 1909 in Dublin. He was the second born of five children within an English family household. With an outbreak of war in 1914, Bacon's father took the family to London where he joined the Ministry of War. During the post-war years, they spent their time between London and Ireland.
Bacon's homophobic family shamed him for his sexuality. His authoritarian father once caught him wearing his mother's clothes and forced him out of the house.
In his youth, Bacon had a habit of repeatedly running away from his school in Cheltenham. By 1926, he found himself in London with little schooling and little money. In 1927, Bacon traveled to Paris and Berlin, visiting the city's homosexual nightclubs. He was highly impressed by Picasso's 1927 exhibition (Galerie Paul Rosenberg) and began to draw and paint while attending the free Academies. The following year, Bacon returned to London where he established himself at Queensbury Mews West, South Kensington.
In 1929, Bacon exhibited his designs after working as an interior designer in the modernist style of Eileen Gray. Before sharing a second studio with painters Jean Sheperd and Roy De Maistre, his works were featured in Studio1. Eric Hall, a businessman, supported Bacon's work and the pair went on to become lovers (1934-50)
Bacon continued to paint with De Maistre, who was an important leadership figure and a practical guide on artistic technique. Bacon was also influenced by Jean Lurçat and Picasso.
1953 was the year of Bacon's first solo exhibition. It was held in a friend's basement at Sunderland House, which was renamed "Transition Gallery". The structures name change was not well received; in response, Bacon destroyed the affiliated paintings. Although his works were rejected by Read for the International Surrealist Exhibition of 1936, Bacon and De Maistre helped organize Young British Painters, which included artists such as Graham Sutherland, Victor Pasmore, among others.
With the coming of war in 1939, Bacon was exempt from military service and released on account of his severe asthma. He spent 1941 painting in Hampshire, before returning to London. From these years, the works which he considered "the beginning of his career" emerged, including the Three Studies for Figures at the Base of a Crucifixion from 1944 (Tate Gallery N06171), which was first shown at the Lefevre Gallery in April 1945. Francis Bacon became central in post-war Soho art. It involved several other artists including Lucian Freud, Michael Andrews, John Deakin, Henrietta Moraes, Isabel Rawsthorne, and others.
On Sutherland's recommendation, Erica Brausen secured Bacon's contract with Hanover Gallery and sold Painting 1946 to the Museum of Modern Art in 1948. Bacon gambled away his earnings at Monte Carlo and as homosexuality remained illegal, he kept an illicit lifestyle in London and France.
Bacon's first post-war solo exhibition included works inspired by Velazquez. His New York debut followed shortly after; the paintings of Popes that had established his reputation fluctuated with those of contemporary figures in suits. Following Bacon's trips to Egypt and South Africa in 1950, a lighter tonality emerged in his paintings of sphinxes & animals.
During this period, Peter Lacey became Bacon's lover and inspired homoerotic images of wrestlers. The idea derived from Eadweard Muybridge's photographs in Animal Locomotion, Animals in Motion, and The Human Figure in Motion. The photographs became customary as the theme of sexual encounters persisted. By 1954 in Italy, Bacon avoided seeing Velazquez's work in Rome and his paintings at the Venice Biennale.
Following Van Gogh's exhibition marked a sudden departure from monochromatic to colorful works. Despite having been successful, Bacon transferred to Marlborough Fine Art, who was willing to pay off his gambling debts, mount larger exhibitions, and ensured that Bacon destroyed fewer canvases.
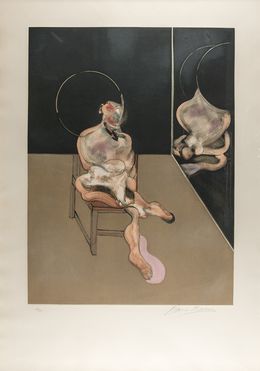
In 1961, Bacon settled in South Kensignton where he stayed for the remainder of his life. The following year, the Tate Gallery organized a major touring retrospective which resumed Bacon's use of the triptych, his most characteristic format. At this time, he also recorded the first of many interviews with critic David Sylvester, establishing canonical text on his work.
Bacon's international reputation was confirmed with his retrospective at the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum in New York, 1963, and the publication of Ronald Alley's catalog.
He refused the 1967 Carnegie Institute Award and donated the Rubens Prize to the restorations following the flood of Florence. On the eve of Bacon's retrospective at the Grand Palais in Paris (1971), his long-time lover George Dyer committed suicide, leaving the event utterly haunted. By 1974, John Edwards became the painter's companion and model.
During this period, Bacon's works were dominated by the triptych. The figures were calm against flat fields of color. His exhibitions climaxed in a second Tate retrospective in 1985. The show traveled to Stuttgart, Berlin, and Moscow in 1988, a sign of post-communist liberalism, then to Washington in 1989.
On a visit to Madrid, Bacon was hospitalized with pneumonia exacerbated by asthma. He died on 28 April 1992.
Nationality
Categories
Artistic movements
Themes